250x250
Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
Tags
- 데코레이터
- fetch
- 동적sql
- 지연로딩
- eager
- JPQL
- execute
- PS
- 힙
- exclusive lock
- 백트래킹
- 스프링 폼
- 비관적락
- shared lock
- SQL프로그래밍
- 유니크제약조건
- CHECK OPTION
- 즉시로딩
- 낙관적락
- 스토어드 프로시저
- 일대다
- 다대다
- 연관관계
- 이진탐색
- BOJ
- querydsl
- FetchType
- 연결리스트
- dfs
- 다대일
Archives
- Today
- Total
흰 스타렉스에서 내가 내리지
[자료구조] 힙 (Heap) 본문
728x90
힙(heap)은 내부 표현이 동적 배열이며 완전 이진 트리이다.
힙에는 최대 힙(max heap)과 최소 힙(min heap)이 있다.
- 최대 힙 (max heap) : 부모노드의 키값이 자식노드의 키값보다 항상 큰 힙
- 최소 힙 (min heap) : 부모노드의 키값이 자식노드의 키값보다 항상 작은 힙
힙 트리

힙 트리의 특징
- index(left_child) = index(parent) * 2
- index(left_child) = index(parent) * 2 + 1
Max Heap 소스코드
class Element:
def __init__(self, key):
self.key = key
class MaxHeap:
# 이 곳에서는 힙의 크기를 최대 100으로 제한하고 있지만,
# 실제 구현에서는 힙이 가득 찼을 때 크기를 2배씩 늘려 가며 계속 요소를 저장한다.
MAX_ELEMENTS = 100
def __init__(self):
self.arr = [None for _ in range(self.MAX_ELEMENTS+1)]
self.heapsize = 0
def is_empty(self):
if self.heapsize == 0:
return True
return False
def is_full(self):
if self.heapsize >= self.MAX_ELEMENTS:
return True
return False
def parent(self, idx):
return idx>>1
def left(self, idx):
return idx<<1
def right(self, idx):
return (idx<<1)+1
def push(self, item):
if self.is_full():
raise IndexError("the heal is full")
# 완전 이진 트리를 유지하기 위해 마지막 원소의 다음 인덱스
self.heapsize += 1
cur_idx = self.heapsize
# cur_idx가 루트가 아니고, item의 key가 cur_idx의 부모의 키보다 크면
while cur_idx != 1 and item.key > self.arr[self.parent(cur_idx)].key:
self.arr[cur_idx] = self.arr[self.parent(cur_idx)]
cur_idx = self.parent(cur_idx)
self.arr[cur_idx] = item
def pop(self):
if self.is_empty():
return None
rem_elem = self.arr[1] # 삭제후 반환 될 원소
# 맨 마지막에 위치한 원소를 받아 온 후 힙사이즈를 줄이면 완전 이진 트리 특성을 유지할 수 있다
temp = self.arr[self.heapsize]
self.heapsize -= 1
cur_idx = 1
child = self.left(cur_idx)
while child <= self.heapsize:
if child < self.heapsize and self.arr[self.left(cur_idx)].key < self.arr[self.right(cur_idx)].key:
child = self.right(cur_idx)
if temp.key >= self.arr[child].key:
break
self.arr[cur_idx] = self.arr[child]
cur_idx = child
child = self.left(cur_idx)
self.arr[cur_idx] = temp
return rem_elem
def print_heap(h):
for i in range(1, h.heapsize+1):
print(f'{h.arr[i].key}', end=' ')
print()
if __name__ == "__main__":
h = MaxHeap()
h.push(Element(2))
h.push(Element(14))
h.push(Element(9))
h.push(Element(11))
h.push(Element(6))
h.push(Element(8))
print_heap(h)
while not h.is_empty():
rem = h.pop()
print(f'poped item is {rem.key}')
print_heap(h)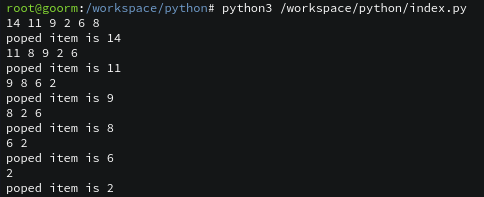
힙은 어디에 쓰이는가?
우선순위 큐를 구현하는데 사용된다.
'Data Structure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Trie 구조 (0) | 2024.01.09 |
|---|---|
| 자료구조에 대하여 (0) | 2022.01.02 |
| [자료 구조] 이진 탐색 트리 (Binary Search Tree) (0) | 2022.01.02 |
| [자료구조] 트리에서의 4가지 순회 방법 (0) | 2022.01.02 |
| [자료구조] 큐와 원형 큐 (Queue, Circular Queue) (0) | 2022.01.02 |

